The drive to establish a colony on Mars comes up against a difficult problem to overcome:building materials. Transporting these from Earth is far too expensive. Recently, researchers have proposed on-site constructions with blood, sweat, tears and urine.
Travelling to Mars, establishing a base there and then a colony raises a lot of questions, the majority of which have not yet found any answers valid. If Elon Musk and other celebrities in the aerospace field dream of establishing a colony on the red planet, one point in particular represents a real obstacle to this kind of project. Indeed, it is totally out of the question to transport building materials from Earth. It must be said that the cost of transporting a single brick between the two planets is estimated at around two million dollars. The colonists will therefore have to use the resources present on site.
Some researchers believe that Martian rocks and soil can be serious leads, like sparse water deposits. However, scientists from the University of Manchester (UK) have mentioned another possible solution. In their study published in the journal Materials Today Bio in September 2021, researchers think of the crew itself as a resource. According to the researchers, human serum albumin – a common blood plasma protein – could act as a binder for Martian (and lunar) dust. The result obtained is nothing but a kind of concrete.
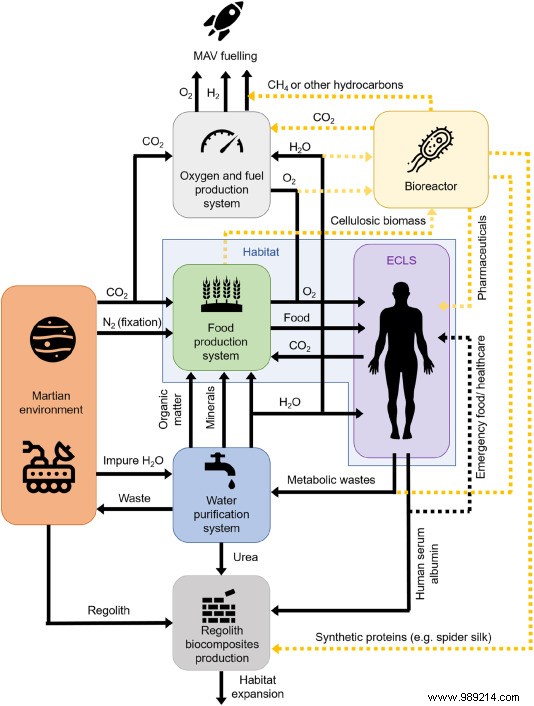
Be aware that albumen has the property of "curdling" (like milk) toform an extended structure . According to the leaders of the study, it is a question of interactions well known to science:the "beta sheets". British researchers have recalled that during human history, animal blood has already been used as a binder for mortar. In other words, one of the solutions allowing the success of the space conquest could be based on a practice dating from the Middle Ages.
During their tests, scientists obtained a material with the name AstroCrete. This one would have a compressive strength of 25 megapascals (MPa), comparable to that of ordinary concrete – between 20 and 32 MPa. However, it is possible to improve this characteristic by incorporating urine, sweat or even tears into the mixture. The material from this mixture would display a compressive strength of 40 MPa! Finally, the leaders of the study estimate that a crew of six astronauts would be able to produce around 500 kg of AstroCrete in the case of a two-year trip.