The "Zhurong" lander and rover of the Tianwen-1 mission, China's first interplanetary expedition, landed on Mars a few days ago . The size of a golf cart, the vehicle will collect data on Martian groundwater. It will also be about mapping the geological structure of the planet.
It's done:on May 15, around 4 a.m. (Beijing time), the Chinese probe Tianwen-1 dropped its lander and its rover - named Zhurong -, completing the most perilous stage of his ten-month mission. A few hours later, the two craft began to slice through the atmosphere of Mars, nestled inside their capsule, at more than four kilometers per second.
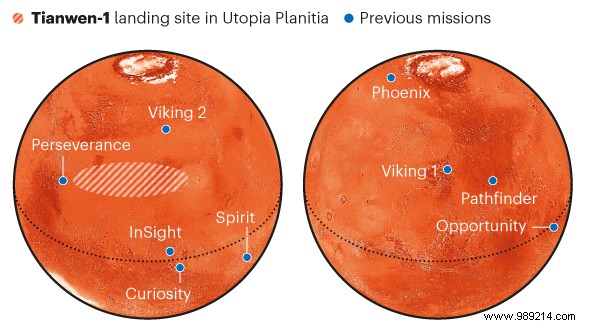
The landing attempt then involved deploying a parachute, firing retrorockets and inflating huge air cushions. The lander finally touched down safely on a vast rocky plain called Utopia Planitia. Only two countries had ever achieved this technical feat:Russia and the United States.
This new successful mission marks once again the incredible progress of the Chinese space program recorded in recent years. Remember that China, which sent its first taikonaut into space in 2003, distinguished itself last year by bringing to Earth the first lunar samples in forty years. A year earlier, China had also successfully landed on the far side of the Moon.
Finally, note that the country is currently building a space station which will succeed the ISS in the coming years.
In a few days, the six-wheeled rover, 1.85 meters long and weighing around 240 kg, will be released on the surface by its lander. Its nominal lifetime is 90 Sols (92.5 Earth days). However, it could survive for years, as NASA's Spirit and Opportunity rovers did. Recall also that Yutu-2, China's rover operating on the far side of the Moon, had a similar design lifespan. However, the vehicle is still active after more than two years.
Utopia Planitia, where Zhurong is located, is a large, relatively flat expanse formed by the impact of an object several billion years ago. The surface of the basin is mainly covered with volcanic material, which could have been modified by more recent processes, such as the repeated freezing and thawing of ice. Also the researchers are particularly excited about the possible detection of permafrost below the surface.
To operate, Zhurong is equipped with several instruments. Two cameras will aim to take images of nearby rocks, while a multispectral camera and a spectrometer equipped with laser technology will study their constitution.
Like Perseverance, Zhurong also offers ground penetrating radar. This instrument will reveal the geological processes that led to the formation of the regions through which it moves.
Meanwhile, the mission's orbiter will take care of transferring data from Zhurong to China. However, the craft will also make its own scientific contributions. In particular, it will be a question of analyzing the border between the upper Martian atmosphere and the solar winds, again to better understand the functioning of the magnetic field of Mars.